Fire Prevention Plan
Purpose and Objectives
The objective of this program is to prevent fires in the workplace and to provide employees with the necessary information to recognize hazards and take appropriate action if a fire does occur. This program will ensure quick, correct, and decisive responses to minimize injury and loss of life. Employees will be informed of this program and trained in response to fires.
This program applies to all employees and all company locations.
Definitions
Alarm System: A system capable of alarming employees by being perceived above ambient noise or light levels by all area employees.
Assembly Point: A previously agreed-upon area near the worksite when employees are instructed to assemble in the event the work site is evacuated.
Combustible Material: A substance that will ignite and burn in the form in which it is used and under anticipated conditions.
Evacuation: The act of exiting the work site in an orderly and expedient manner.
Flammable Material: A substance that can easily catch fire but does not ignite as readily as a combustible material.
Incipient Fire: A flame that is in the initial or beginning stage which can be controlled or extinguished by portable fire extinguishers.
Responsible Person: An employee responsible for managing the Fire Prevention Program. This individual shall maintain training records and ensure the program is kept up to date on an annual basis.
Note: Whitley Maddox, Director of Human Resources, Safety, and Environmental is Cherokee’s responsible person.
Responsibilities
The company will provide adequate controls and equipment to aid in fire prevention and also in fighting fire safely.
Management will ensure proper adherence and support of this program and ensure fire extinguisher training is administered
The program manager will be responsible for compiling and maintaining a list of all significant fire hazards in the workplace, the job titles of personnel responsible for fire prevention and control, developing procedures for use and care of equipment, and developing proper training. The program manager must also understand the work practices of employees that may create fire hazards as well as workplace conditions that may make the facility more vulnerable to fires.
Note: Whitley Maddox, Director of Human Resources, Safety, and Environmental is Cherokee’s program manager.
Employees are responsible for following the procedures outlined in this program.
Determination of Major Fire Hazards
The company will determine the fire hazards in the workplace and then identify steps to mitigate the risk and prevent fires from occurring. To identify fire hazards, the fire triangle may be utilized to identify sources of heat, fuel, and oxygen which must all be in place for a fire to occur.
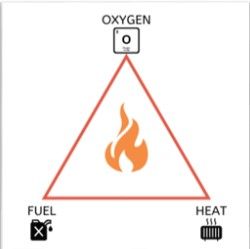
Figure 1 The Fire Triangle
Storage and Handling Procedures
Those materials that have been determined to be flammable or combustible will be arranged to ensure adequate clearance is maintained from ignition sources such as heating surfaces, HVAC ducts, heaters, and lighting fixtures. All storage containers of flammables should be labeled appropriately. Flammable storage cabinets shall be separated from other materials in storage and separated so that only compatible materials are stored together.
Containers used for flammable or combustible materials must be designed, constructed, and tested according to regulations.
Compressed gas cylinders must be secured in place and stored away from heat or ignition sources. Pressurized gas cylinders should never be used without pressure regulators.
Ordinary combustibles such as pallets should not be stacked over 6 feet in height. If feasible, extra materials that cannot meet this standard shall be stored in a separate area to reduce the build-up or accumulation of combustible materials. Piles of combustibles such as trash, scrap wood, or paper should not be stored near buildings and should also be located far enough from each other to allow for firefighting efforts in the event of a fire.
Small quantities of flammables or combustible materials such as lab, chemical, or process chemicals shall be stored in and dispensed from approved safety containers. Any flammable liquids will be stored away from sources that can produce sparks. These containers must include positive ventilation.
Potential Ignition Sources
Potential ignition sources will be identified by the company. In addition, the following precautions must be made to prevent ignition sources from resulting in fires:
- Electrical fuses can potentially cause sparks and should never be misused. Never install a fuse rated higher than the specified circuit.
- Electrical equipment should be monitored and, if damage occurs to wiring, switches, or elements, appropriate maintenance should be conducted.
- The use of extension cords should be carefully managed and should not ever include connecting heating devices.
- Welding or cutting should be prohibited unless all tenants of the Hot Work system are followed.
- Ensure that all utility lights are not positioned near flammables and that they include a wire guard over the light face.
- Appliances such as space heaters must be monitored. It is recommended that all space heaters in the facility have automatic shutdown safety devices in case they are tipped.
Housekeeping and Prevention of Accumulation
Housekeeping is a critical part of the Fire Prevention Program. The accumulation of materials is a known contributor to fires in the workplace and should not be overlooked. The following list contains housekeeping measures to prevent fires:
- Keep storage areas and working areas free of trash and debris.
- Place oily rags only in covered containers and dispose of daily.
- Ensure that flammable and combustible materials are stored properly when not in use.
- If an employee’s clothing becomes contaminated with flammable liquids, the employee must change prior to returning to work.
- Verify that electrical circuits are not overloaded.
- Turn off any non-essential equipment at the end of the day.
- Ensure that escape routes, doorways, and walkways are unobstructed. Stairwell doors are not to be left open and material may never be stored in stairwells.
- Do not allow materials to be stored in a way that obstructs or blocks fire sprinkler heads. A minimum of 18 inches of clear space must be maintained below sprinkler heads at all times.
Fire Protection Equipment
Alarm Systems
The fire alarm system will be available and maintained to sound at a level which can be heard above ambient noise conditions throughout the workplace. The fire alarm will also be set to transmit to a local fire department automatically
The automatic sprinkler system will adhere to applicable National Fire Protection Agency (NFPA 13) standards for the installation of sprinkler systems. The sprinkler system will be appropriate for the type of work and storage of flammables in the work area. All systems will be maintained according to NFPA specifications.
Fire Extinguishers
Portable fire extinguishers will be placed at regular intervals in all buildings. In areas where the risk of fire is elevated, these will be placed in response to the hazard present. Fire extinguishers must be inspected monthly and always be in clear sight. Fire extinguishers used may be any one of the four classes of extinguisher and will be chosen based on the fuel sources present.
- Class A Fire Extinguishers will be used on ordinary combustibles or fibrous material such as wood, paper, cloth, rubber, and certain types of plastic. The travel distance for employees to access extinguishers must be 75 feet or less.
- Class B Fire Extinguishers will be used for flammable or combustible liquids such as gasoline, kerosene, paint, thinners, and propane. Travel distance to reach Class B extinguisher must be 50 feet or less.
- Class C Fire Extinguishers will be used for electrical equipment such as panel boxes, appliances, electrical rooms, and appliances. Travel distance to Class C extinguishers must be less than 50 feet.
- Class D Fire Extinguishers will be used on combustible metals such as titanium, magnesium, and sodium. The travel distance for Class D extinguishers must be 75 feet or less.
Note: Cherokee uses Class ABC Fire Extinguishers in all areas except specific locations that are better protected by Class C extinguishers.
Access to provided fire-fighting equipment shall be maintained at all times and conspicuously located. The placement of fire extinguishers should ensure they are mounted higher than 4 feet from the floor. Equipment will be inspected periodically to ensure it is maintained in operating condition. Any defective equipment will be immediately replaced. Locations of all fire extinguishers, hydrants, and hoses shall be appropriately marked. Fire extinguisher maintenance should include the following:
- Identity number to indicate the assigned location of the extinguisher
- Checks to ensure the extinguisher is charged and in operable condition
- Inspection to determine if the extinguisher is clean and free from defects
- Area survey to confirm that the path to the extinguisher is clear and readily accessible
Fire extinguishers will be inspected visually on a monthly basis and also receive an annual maintenance check by certified personnel. Fire extinguishers will also be recharged and recertified or replaced after any use. If a fire extinguisher inspection indicates a loss of pressure, the extinguisher will be removed from service and replaced. Fire extinguisher logs will be maintained for 5 years.
Fire Detection Systems
In areas where fire detection systems are in use, all systems will be maintained and in operable use at all times. Fire detectors and detection systems will be tested and maintained to ensure proper reliability. Inspections will be conducted periodically to ensure that fire detectors are clean and free from dust and other particulates. All service and maintenance conducted on the system will be performed by trained and knowledgeable technicians. No fire detection system setting will delay an alarm for more than 30 seconds.
Fire Suppression Systems
Installed fire suppression systems will meet the requirements of OSHA 1910.159 unless they are installed in workplaces in which suppression systems are not required by OSHA. In such cases they will be exempt.
Use of Fire Protection Equipment
In the event of a fire, no employee is required to fight the fire. Only small fires that can easily be extinguished should be fought and, in all other cases, employees should immediately evacuate. Only those employees who have been trained in the use of fire-fighting equipment should attempt to fight a fire. Those employees who have been trained should follow the instructions below for the safe use of a fire extinguisher.
Fire Extinguisher Use
If a fire occurs, employees trained in the use of fire extinguishers may attempt to extinguish the fire if it is still in an incipient state. All other employees will begin evacuation.
The employee who is attempting to extinguish the fire will use the PASS method as outlined below:
- P – Pull the safety pin at the top of the extinguisher
- A – Aim the nozzle of the extinguisher at the base of the flames
- S – Squeeze the handle to dispense the extinguishing agent
- S – Sweep the nozzle from side to side at the base of the flames until the fire is out
If the fire extinguisher has been fully discharged but the flames are still visible, the employee that is fighting the fire should evacuate.
If it appears that the fire is completely extinguished, continue to monitor the area and ensure that heat has dissipated.
Evacuation Procedures
Evacuation routes and maps will be created and posted in each work area. The following information shall be available on evacuation maps:
- Emergency exits
- Primary and secondary evacuation routes
- Locations of fire extinguishers
- Locations of fire alarm pull station locations
- Assembly points
Each employee will be instructed for at least two separate evacuation routes from their primary work area. The maps will be updated when changes occur in the workplace that effect the locations or suggested evacuation routes. These routes should avoid routing traffic through work areas that may become more dangerous in the event of an emergency such as in front of flammable storage areas. Elevators are not to be used in case of an emergency.
Alarms may be utilized to alert occupants of the building to an emergency. If there is not an alarm present in the building, the alarm will be given orally. If employees can activate an alarm system, locations of these systems should be marked on the evacuation route map. If an emergency exists, the first person that identifies the emergency must give the alarm and respond.
In the event an emergency evacuation is initiated through the use of a specified alarm system, total and immediate evacuation of all employees in affected areas will take place. If the evacuation is localized and does not apply to the entire facility, management will determine which areas are to be evacuated or whether to evacuate the entire facility. This will be dependent on the degree of the hazard.
Supervisors are responsible for guiding their employees during the event of an evacuation. Their duties will include swiftly leading employees from danger to a safe assembly point. Once there, they must ensure safety and conduct a head count at the assembly point and inform emergency crews of anyone missing. Then they will work to provide guidance, ensure employees stay in place until further instruction, and provide or assist with first aid if necessary. Under no circumstances are employees to be allowed to re-enter a facility until it has been deemed safe to do so.
The company will ensure employees are accounted for in the event of an emergency evacuation through the use of supervisor-conducted headcounts at the assembly point in the event of an evacuation. Each supervisor will take a count of employees gathered at the assembly point and inform rescue teams as soon as possible of any missing persons
Visitors on site will be accounted for by using sign-in/sign-out sheets when they arrive on site. In the event of an evacuation, a sign-in/sign-out sheet will be used at the assembly point and all visitors will be accounted for as well as the notification of emergency crews of any individuals who are found to be missing.
Training
Training will be provided on this Fire Prevention Program for any employee initially upon hiring and yearly thereafter. Retraining will be administered if employees are assigned a new role where different fire protection and prevention procedures are required, the employee demonstrates a lack of proficiency, or new fire protection and prevention methods and procedures are introduced. The training will include:
- General principles of a fire
- Fire extinguisher use
- Fire extinguisher types
- When to cease extinguisher use and evacuate
- Incipient fires
- Regularly scheduled drills
- Correct storage of flammable and combustible materials
- Safe handling of compressed gases
- Methods to contain spills
- Testing of the alarm systems
Evacuation drills will be conducted periodically. Training records shall be kept for each employee after training is completed
Recordkeeping
Fire equipment inspection records will be maintained for 5 years.
All training will be documented, and records retained. An employee’s understanding of the use of fire extinguishers will be subject to a hands-on test. Training documentation must be comprehensive and will include:
- Topic of training
- Trainer(s)
- Trainer qualifications
- Date of training
- Employee name and job title
- Outline of training provided
The annual program review and document updates must be maintained indefinitely.
