Respiratory Protection Program
Purpose and Objective
This program is intended to provide clear guidance for employees and supervisors in order to ensure the use of respirators is properly implemented, managed, and maintained.
The Respiratory Protection Program applies to all employees, contractors, and others who work on company sites who must use respiratory protection.
Definitions
ANSI: The American National Standards Institute which is the primary organization for the development of technology standards in the United States.
Exposure: An employee who is subjected in the course of employment to a chemical which is a physical or health hazard.
Hazardous Chemical: Any chemical which is classified as a physical or health hazard: a simple asphyxiant, combustible dust, pyrophoric gas, or hazard not otherwise classified.
Physician or Other Licensed Health Care Professional (PLHCP): An individual whose legally permitted scope of practice (i.e., license, registration, or certification) allows him or her to independently provide, or be delegated the responsibility to provide, some or all of the health care services required by paragraph (e) of 29 CFR 1910.134.
Responsibilities
Management
The Respiratory Protection Program should be managed based on hazards present at the worksite. Anyone who uses respirators in their role should understand the limitations of protective equipment and how to ensure it is used correctly for greater effectiveness. The following responsibilities help to ensure this program is effective.
The program administrator has authority over the Respiratory Protection Program and is responsible for:
- Establishing procedures for selecting respirators
- Arranging employee medical evaluations
- Developing procedures for fit testing of all respirators
- Developing procedures and schedules for inspecting, cleaning, maintaining, repairing, and storing respirators
- Developing procedures for self-contained breathing apparatuses (if used)
- Ensuring employees receive proper training
- Evaluating the Respiratory Protection Program periodically for effectiveness
*Note: The Program Administrator- Whitley Maddox, Director of Human Resources, Safety and Environmental
Supervisors are responsible for ensuring that their employees are provided the necessary respirators, that hazard assessments are completed, and that employees follow the requirements of this program. The responsibilities listed below are the responsibilities of supervisors:
- Providing PPE
- Training employees and ensuring that they demonstrate competency in the proper use, maintenance, and storage of respirators
- Notifying the program administrator if new needs for respirators arise
- Notifying the program manager if existing respirators are not meeting the needs of employees
- Ensuring that damaged or ineffective respirators are replaced
Employees who wear respirators must use them in accordance with the instructions and training provided. Employees are also responsible for maintaining their respirators and ensuring they are properly stored when not in use. Additional responsibilities include:
- Wearing assigned respirators
- Attending and participating in training sessions
- Caring for, maintaining, cleaning, and storing respirators appropriately
- Following program policies and rules
- Informing a supervisor of issues associated with respirators or respiratory protection concerns
- Disposing of ineffective or damaged respirators properly
*Note: If Respirator malfunctions, immediately leave the area and inform supervisor. Get a new respirator.
Hazard Identification
The company will identify and evaluate all workplaces for respiratory hazards. That evaluation will include an estimate of the potential exposure of employees to the hazards and will also identify the hazard’s chemical state and physical form.
Air monitoring will be used as necessary to identify levels of exposure agents, including oxygen-deficient atmospheres, and will help to ensure correct respirator selection based on exposure potential.
Collect Information
The first step in hazard identification is to collect existing information about workplace hazards. This collection of information happens in a variety of ways including collecting SDS’s (safety data sheets), audit and inspection reports, previous injury logs, and input from workers. It is also important to gather information from the company’s written safety and health programs, OSHA or NIOSH websites, and trade associations.
Inspect the Workplace
The next step in hazard identification is to inspect the workplace for hazards that have been introduced over time or as the workflow or work processes change. This inspection will be conducted in the form of an audit, which should be conducted regularly and should involve employees. Setting aside time to inspect the workplace on a regular basis identifies problems so they can be addressed before an incident occurs. It is also a good time to confirm that hazardous conditions that were previously recognized have been corrected. Use checklists to highlight items that should be part of the inspection such as:
- Chemical agents
- Biological agents
- Physical agents
- General housekeeping
- Equipment operation
- Equipment maintenance
- Fire protection
- Fall protection
- Work process flow
- Work practices
- Emergency procedures
Not only is hazard identification a good process for existing equipment, but it should also be utilized prior to changing workflow or introducing new equipment. Even conflicting work schedules should be evaluated as a potential hazard that can be mitigated. Hazard assessments will be considered whenever the following take place:
- Facility modifications
- New chemicals are introduced
- New equipment is installed
- Work practices change
- Equipment maintenance changes
- New safety and health information is received
Hazards Associated with Emergency or Non-Routine Situations
Although all preventative actions are to be taken in order to reduce the likelihood of emergencies, it is important to plan for the unexpected and be prepared in case an emergency does occur in the workplace. This should involve identifying possible emergency scenarios including employee health situations, fires, or non-routine shut down of equipment and procedures to respond safely should be developed..
Some situations to consider may include:
- Fires and explosions
- Chemical releases
- Hazardous material spills
- Startups or unplanned shutdowns
- Non-routine tasks
- Natural disasters
- Weather emergencies
- Medical emergencies
Conducting emergency planning exercises such as drills or “tabletop” exercises should be done on a regular basis by each department.
Determine and Prioritize Hazard Controls
After hazards have been identified, the information collected must be used to determine which controls to implement and to set priorities for the timely implementation of them. This prioritization must be conducted by evaluating each hazard and considering the possible severity of the outcomes, likelihood of the event, and number of workers exposed.
Once the severity is determined, the greatest risks should be addressed first. However, it is important not to stop at the greatest risk but to continue mitigating hazards so that continuous improvement can be achieved. For those controls that need a more extensive timeline to sustainably control (equipment modifications, engineering designs), control measures must be implemented in the interim to protect workers.
Hazard Prevention and Control
Hazard prevention and control must be implemented when hazards are recognized in the workplace. Hazard prevention is a process and often may involve several steps, including:
- Identifying potential options for controlling hazards
- Using a hazard control plan to guide selection and implementation of controls
- Developing plans to protect workers during emergencies
- Evaluating the effectiveness once implemented to determine if additional controls are necessary
Identifying control measures for a recognized hazard can involve a variety of methods such as using manufacturer’s suggestions, training, substituting one chemical for another, getting input from workers, etc. Hazard control options will fall into one of the following categories: elimination, substitution, engineering, administrative, or PPE.
Respirator Selection
The company will evaluate and select the proper respirators by determining whether there is a potential for employees to be exposed to contaminants at the permissible exposure limits (PEL) or if there is another specific reason an employee elects such protection.
Filters and cartridges must be matched to the anticipated atmospheric contaminants. A variety of respirator sizes must be kept in stock and available to ensure a proper fit for all employees. Only respirators certified by the National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) based on the criteria in Table 1 below from OSHA 1910.134 and 1926.103 will be used.
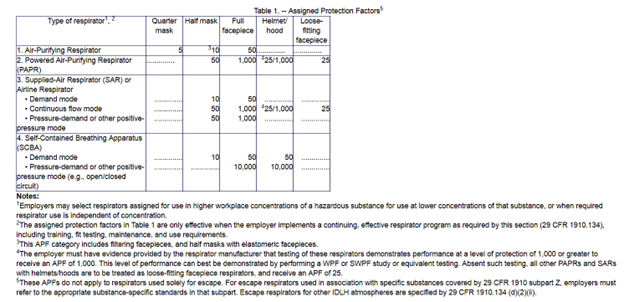
When determining the assigned protection factors (APFs), the company will use Table 1 for APFs in atmospheres that are not considered immediately dangerous to life and health (IDLH).
Should entry into an IDLH atmosphere be required, a site-specific respiratory protection program will be developed for the IDLH hazards with specific equipment and training for affected employees. Such a program will be separate from this program and will fully address the hazards and controls needed to maintain the safety and health of our employees.
Voluntary Respirator Usage
The company will provide or allow employee-owned respirators for voluntary usage.
The company will provide all employees who voluntarily choose to wear respirators with a copy of Appendix D of this document. Employees who choose to wear respirators that are air-purifying in half-face or more protective models must comply with the procedures for medical evaluation, respirator use and cleaning, maintenance, and storage.
The company shall authorize voluntary use or respiratory protective equipment as requested by all other workers on a case-by-case basis, depending on the specific workplace conditions and the results of medical evaluations.
Medical Evaluations
Each employee required to wear a respirator or who requests an air-purifying respirator must be medically evaluated before being fit-tested. The company will arrange for each employee to have a medical evaluation by a physician or other licensed health care professional (PLHCP). The company will provide a copy of the OSHA Respirator Medical Evaluation Questionnaire (Appendix A) to each employee who must wear respirators and will collect completed questionnaires and provide them to the PLHCP.
*Medical exams are performed by a physician at Macon Occupational Medicine.
The PLHCP must also be provided with the following information:
· Type and weight of respirator each employee will use
· Duration and frequency of use
· Expected physical work effort
· Any other protective equipment anticipated and clothing needed
· Temperature and humidity extremes at the job site
· Air contaminants and concentration levels that each employee may encounter.
The PLHCP will discuss the results of the evaluation with the employee and provide a written determination to the company. The determination will contain confidential medical information but will include:
· The PLHCP’s opinion of the employee’s ability to tolerate a respirator
· Any limitations of respirator use
· Any need for follow-up evaluations
· A statement that the employee has been informed of the determination
If the PLHCP recommends alternative respiratory protection, such as a powered air purifying respirator, the company will comply with the recommendation.
The company will maintain a file of the PLHCP’s written determination for each employee. Employees will receive follow-up medical evaluations under the following conditions:
· The employee reports medical signs or symptoms related to the use of the respirator
· The PLHCP, supervisor, or program administrator recommends a re-evaluation
· Fit test or other program information indicates a need for re-evaluation
· Changes in the workplaces increase respiratory stress
The company will provide additional medical evaluations if:
· An employee reports symptoms that are related to or can cause complications in the ability to use a respirator
· A PLHCP or the respirator program administrator informs the company that the employee should be re-evaluated
· Information indicates the employee needs a re-evaluation
· A change occurs in the workplace conditions
Fit Testing
All employees using a tight-fitting face-piece respirator must pass an appropriate qualitative fit test (QLFT) or quantitative fit test (QNFT). The program administrator will determine which test is appropriate for each type of respirator. Qualitative and quantitative fit tests will be administered with the appropriate protocol from 29 CFR 1910.134 or 29 CFR 1926.103.
Employees must be fit tested before they use a respirator for the first time, whenever they use a different or new respirator face piece, and after any changes in physical condition that could affect the respirator fit.
Fit tests will be administered using an employee’s assigned respirator (from previous fit testing results) or from a selection of respirators set up for fit testing purposes (for an initial fit test).
All employees must be fit tested annually.
Note: At Cherokee Brick we use Qualitative Fit Test. (see attached)
Fit Test Procedures
Fit tests may be conducted using qualitative or quantitative methods. The employee must be provided with the most acceptable respirator size in order to obtain the correct fit. The employee undergoing a fit test must be able to wear the chosen face piece at least five minutes in comfort. The following points can be used for evaluation:
· Donning the mask several times to become comfortable with wearing and properly adjusting
· Positioning the mask on the nose
· Ensuring room for eye protection
· Validating there is room to talk
· Ensuring a good fit on the face and cheeks
The following will be used to determine fit:
· Adequate and comfortable strap tension
· Fit across the bridge of the nose
· Respirator chin properly placed
· Respirator properly sized from nose to chin
· The tendency of the respirator to slip
· Employee self-observation
Respirator Seal Check
The employee shall be guided in conducting seal checks to ensure the respirator properly seals outside air and is only pulling air in through cartridges. This should be conducted first by seating the mask and breathing in, moving the head up and down and side to side, and taking slow, deep breaths.
Next, a positive and negative pressure check shall be conducted as well as test exercises which are deemed the most appropriate such as reading the rainbow passage or irritant smoke tests.
Respirator Use
Using Tight-Fitting Respirators
Employees who have beards or other conditions that interfere with the face-to-face seal or valve function cannot wear tight-fitting respirator face pieces. Clean-shaven skin must be in contact with all respirator sealing surfaces. PPE or clothing that interferes with the face-to-face seal or valve function is not permitted.
Corrective lenses (eyeglasses) with temple bars or straps that interfere with face-to-face sealing areas cannot be used with any respirator.
Each employee must perform a user seal check before putting on a tight-fitting respirator.
Monitoring Respirator Effectiveness
The program administrator will monitor and re-evaluate the effectiveness of the respirator program after any significant changes in the workplace condition or exposure levels.
Employees must leave the areas in which they wear respirators when:
· They need to wash their faces or their respirator face piece components
· They detect face piece leaks or change in breathing resistance
· They must change respirator filters, cartridges, or canister elements
Respirator Maintenance, Cleaning, and Care
Before any new respirator is used, it must be washed, disinfected, and inspected according to the manufacturer’s instructions or the instructions in Appendix B.
Employees must clean and disinfect their own respirators after each use and store them in a sanitary location, so the face pieces and valves are protected.
Respirators used for fit testing must be cleaned and disinfected after each use by the person conducting the fit test.
Employees must inspect their respirators before they use them and after they clean them. Inspection includes:
· A check of respirator function
· Tightness of connections
· The condition of the elastomeric face piece, head straps, valves, connecting tubes, cartridges, canisters, and filters
Only trained employees can replace worn or deteriorated respirator parts. All repair work, adjustments, and replaced parts must comply with the respirator manufacturer’s instructions.
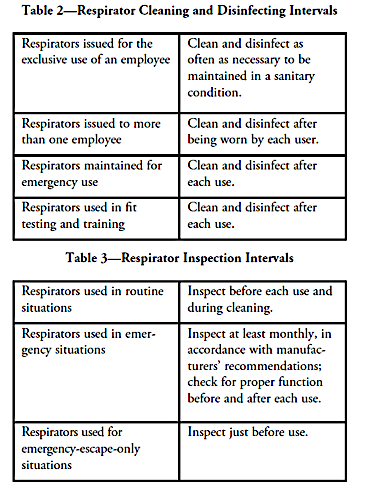
Tables 2 and 3 below from OSHA 1910.134 show the required intervals for cleaning, disinfection, and inspecting respirators. Appendix B describes respirator cleaning procedures.
Identity of Filters, Cartridges, and Canisters
All filters, cartridges, and canisters must be maintained as received by the manufacturers, distributor, or suppliers and labeled and color-coded with the NIOSH-approval label. The label cannot be removed and must remain legible. Defective filters, canisters, and cartridges cannot be used and must be removed from service.
Air Quality in Atmosphere-Supplying Respirators
Compressed breathing air used in atmosphere-supplying respirators must meet the criteria established by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) for Grade D Breathing Air.
Training Requirements
After it has been determined that respiratory protection is required, the employer must provide the equipment to employees and train them prior to performing hazardous tasks. Before any employee wears a respirator for the first time, he or she must receive training on and demonstrate comprehension of:
· Why a respirator is necessary
· How improper fit, use, or maintenance can compromise the protective effect of a respirator
· A respirator’s capabilities and limitations
· How to use a respirator in emergency situations, including ones in which a respirator malfunctions
· How to inspect, put on, and remove a respirator and check the seals
· Proper maintenance and storage procedures
· How to recognize medical signs and symptoms that may limit or prevent effective respirator use
Training will be provided by the program administrator or another qualified person. The training must be fully documented and certify that employees understand the concepts presented and have demonstrated how to use and wear the respirator.
Training must give each user an opportunity to handle the respirator, have it fitted, test the seal, and wear it in normal air for a trial period.
Retraining
Retraining must be performed annually and also when deemed necessary due to changes in the workplace, program evaluations, or employee performance.
Employees who are responsible for inspecting the emergency and supplied-air respirators will receive supplied-air respirator specific training.
Retraining of employees is required when:
· Changes in the workplace occur that make previous training obsolete
· Changes in the type of PPE occur
· Employer observes inadequacies in an employee’s performance based on demonstrated use of assigned PPE that indicates an employee has not retained the necessary understanding or skill
Employees who are permitted to wear respirators must first read the information in Appendix C.
Recordkeeping
This program will be reviewed periodically to ensure compliance is maintained. The Program Administrator will maintain records of non-confidential medical evaluation determinations, fit testing, training documentation, and annual inspection audits and will make them available to employees.
All employee medical records must be maintained for the duration of employment +30 years.
Appendix
Appendix D to § 1910.134 (Mandatory) Information for Employees Using Respirators When Not Required Under the Standard
Respirators are an effective method of protection against designated hazards when properly selected and worn. Respirator use is encouraged, even when exposures are below the exposure limit, to provide an additional level of comfort and protection for workers. However, if a respirator is used improperly or not kept clean, the respirator itself can become a hazard to the worker. Sometimes, workers may wear respirators to avoid exposures to hazards, even if the amount of hazardous substance does not exceed the limits set by OSHA standards. If your employer provides respirators for your voluntary use, or if you provide your own respirator, you need to take certain precautions to be sure that the respirator itself does not present a hazard.
You should do the following:
- Read and heed all instructions provided by the manufacturer on use, maintenance, cleaning and care, and warnings regarding the respirators limitations.
- Choose respirators certified for use to protect against the contaminant of concern. NIOSH, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, certifies respirators. A label or statement of certification should appear on the respirator or respirator packaging. It will tell you what the respirator is designed for and how much it will protect you.
- Do not wear your respirator into atmospheres containing contaminants for which your respirator is not designed to protect against. For example, a respirator designed to filter dust particles will not protect you against gases, vapors, or very small solid particles of fumes or smoke.
- Keep track of your respirator so that you do not mistakenly use someone else's respirator.
[63 FR 1152, Jan. 8, 1998; 63 FR 20098, April 23, 1998]
Appendix B-1 to § 1910.134: User Seal Check Procedures (Mandatory)
The individual who uses a tight-fitting respirator is to perform a user seal check to ensure that an adequate seal is achieved each time the respirator is put on. Either the positive and negative pressure checks listed in this appendix, or the respirator manufacturer's recommended user seal check method shall be used. User seal checks are not substitutes for qualitative or quantitative fit tests.
I. Facepiece Positive and/or Negative Pressure Checks
A. Positive pressure check. Close off the exhalation valve and exhale gently into the facepiece. The face fit is considered satisfactory if a slight positive pressure can be built up inside the facepiece without any evidence of outward leakage of air at the seal. For most respirators this method of leak testing requires the wearer to first remove the exhalation valve cover before closing off the exhalation valve and then carefully replacing it after the test.
B. Negative pressure check. Close off the inlet opening of the canister or cartridge(s) by covering with the palm of the hand(s) or by replacing the filter seal(s), inhale gently so that the facepiece collapses slightly, and hold the breath for ten seconds. The design of the inlet opening of some cartridges cannot be effectively covered with the palm of the hand. The test can be performed by covering the inlet opening of the cartridge with a thin latex or nitrile glove. If the facepiece remains in its slightly collapsed condition and no inward leakage of air is detected, the tightness of the respirator is considered satisfactory.
II. Manufacturer's Recommended User Seal Check Procedures
The respirator manufacturer's recommended procedures for performing a user seal check may be used instead of the positive and/or negative pressure check procedures provided that the employer demonstrates that the manufacturer's procedures are equally effective.
[63 FR 1152, Jan. 8, 1998]
Appendix B-2 to § 1910.134: Respirator Cleaning Procedures (Mandatory)
These procedures are provided for employer use when cleaning respirators. They are general in nature, and the employer as an alternative may use the cleaning recommendations provided by the manufacturer of the respirators used by their employees, provided such procedures are as effective as those listed here in appendix B-2. Equivalent effectiveness simply means that the procedures used must accomplish the objectives set forth in appendix B-2, i.e., must ensure that the respirator is properly cleaned and disinfected in a manner that prevents damage to the respirator and does not cause harm to the user.
I. Procedures for Cleaning Respirators
A. Remove filters, cartridges, or canisters. Disassemble facepieces by removing speaking diaphragms, demand and pressure-demand valve assemblies, hoses, or any components recommended by the manufacturer. Discard or repair any defective parts.
B. Wash components in warm (43 °C [110 °F] maximum) water with a mild detergent or with a cleaner recommended by the manufacturer. A stiff bristle (not wire) brush may be used to facilitate the removal of dirt.
C. Rinse components thoroughly in clean, warm (43 °C [110 °F] maximum), preferably running water. Drain.
D. When the cleaner used does not contain a disinfecting agent, respirator components should be immersed for two minutes in one of the following:
1. Hypochlorite solution (50 ppm of chlorine) made by adding approximately one milliliter of laundry bleach to one liter of water at 43 °C (110 °F); or,
2. Aqueous solution of iodine (50 ppm iodine) made by adding approximately 0.8 milliliters of tincture of iodine (6-8 grams ammonium and/or potassium iodide/100 cc of 45% alcohol) to one liter of water at 43 °C (110 °F); or,
3. Other commercially available cleansers of equivalent disinfectant quality when used as directed, if their use is recommended or approved by the respirator manufacturer.
E. Rinse components thoroughly in clean, warm (43 °C [110 °F] maximum), preferably running water. Drain. The importance of thorough rinsing cannot be overemphasized. Detergents or disinfectants that dry on facepieces may result in dermatitis. In addition, some disinfectants may cause deterioration of rubber or corrosion of metal parts if not completely removed.
F. Components should be hand-dried with a clean lint-free cloth or air-dried.
G. Reassemble facepiece, replacing filters, cartridges, and canisters where necessary.
H. Test the respirator to ensure that all components work properly.
[63 FR 1152, Jan. 8, 1998]
Appendix C to § 1910.134: OSHA Respirator Medical Evaluation Questionnaire (Mandatory)
To the employer: Answers to questions in Section 1, and to question 9 in Section 2 of part A, do not require a medical examination.
To the employee:
Your employer must allow you to answer this questionnaire during normal working hours, or at a time and place that is convenient to you. To maintain your confidentiality, your employer or supervisor must not look at or review your answers, and your employer must tell you how to deliver or send this questionnaire to the health care professional who will review it.
Part A. Section 1. (Mandatory) The following information must be provided by every employee who has been selected to use any type of respirator (please print).
1. Today's date:_______________________________________________________
2. Your name:__________________________________________________________
3. Your age (to nearest year):_________________________________________
4. Sex (circle one): Male/Female
5. Your height: __________ ft. __________ in.
6. Your weight: ____________ lbs.
7. Your job title:_____________________________________________________
8. A phone number where you can be reached by the health care professional who reviews this questionnaire (include the Area Code): ____________________
9. The best time to phone you at this number: ________________
10. Has your employer told you how to contact the health care professional who will review this questionnaire (circle one): Yes/No
11. Check the type of respirator you will use (you can check more than one category):
a. ______ N, R, or P disposable respirator (filter-mask, non-cartridge type only).
b. ______ Other type (for example, half- or full-facepiece type, powered-air purifying, supplied-air, self-contained breathing apparatus).
12. Have you worn a respirator (circle one): Yes/No
If "yes," what type(s):___________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
Part A. Section 2. (Mandatory) Questions 1 through 9 below must be answered by every employee who has been selected to use any type of respirator (please circle "yes" or "no").
1. Do you currently smoke tobacco, or have you smoked tobacco in the last month: Yes/No
2. Have you ever had any of the following conditions?
a. Seizures: Yes/No
b. Diabetes (sugar disease): Yes/No
c. Allergic reactions that interfere with your breathing: Yes/No
d. Claustrophobia (fear of closed-in places): Yes/No
e. Trouble smelling odors: Yes/No
3. Have you ever had any of the following pulmonary or lung problems?
a. Asbestosis: Yes/No
b. Asthma: Yes/No
c. Chronic bronchitis: Yes/No
d. Emphysema: Yes/No
e. Pneumonia: Yes/No
f. Tuberculosis: Yes/No
g. Silicosis: Yes/No
h. Pneumothorax (collapsed lung): Yes/No
i. Lung cancer: Yes/No
j. Broken ribs: Yes/No
k. Any chest injuries or surgeries: Yes/No
l. Any other lung problem that you've been told about: Yes/No
4. Do you currently have any of the following symptoms of pulmonary or lung illness?
a. Shortness of breath: Yes/No
b. Shortness of breath when walking fast on level ground or walking up a slight hill or incline: Yes/No
c. Shortness of breath when walking with other people at an ordinary pace on level ground: Yes/No
d. Have to stop for breath when walking at your own pace on level ground: Yes/No
e. Shortness of breath when washing or dressing yourself: Yes/No
f. Shortness of breath that interferes with your job: Yes/No
g. Coughing that produces phlegm (thick sputum): Yes/No
h. Coughing that wakes you early in the morning: Yes/No
i. Coughing that occurs mostly when you are lying down: Yes/No
j. Coughing up blood in the last month: Yes/No
k. Wheezing: Yes/No
l. Wheezing that interferes with your job: Yes/No
m. Chest pain when you breathe deeply: Yes/No
n. Any other symptoms that you think may be related to lung problems: Yes/No
5. Have you ever had any of the following cardiovascular or heart problems?
a. Heart attack: Yes/No
b. Stroke: Yes/No
c. Angina: Yes/No
d. Heart failure: Yes/No
e. Swelling in your legs or feet (not caused by walking): Yes/No
f. Heart arrhythmia (heart beating irregularly): Yes/No
g. High blood pressure: Yes/No
h. Any other heart problem that you've been told about: Yes/No
6. Have you ever had any of the following cardiovascular or heart symptoms?
a. Frequent pain or tightness in your chest: Yes/No
b. Pain or tightness in your chest during physical activity: Yes/No
c. Pain or tightness in your chest that interferes with your job: Yes/No
d. In the past two years, have you noticed your heart skipping or missing a beat: Yes/No
e. Heartburn or indigestion that is not related to eating: Yes/No
f. Any other symptoms that you think may be related to heart or circulation problems: Yes/No
7. Do you currently take medication for any of the following problems?
a. Breathing or lung problems: Yes/No
b. Heart trouble: Yes/No
c. Blood pressure: Yes/No
d. Seizures: Yes/No
8. If you've used a respirator, have you ever had any of the following problems? (If you've never used a respirator, check the following space and go to question 9:)
a. Eye irritation: Yes/No
b. Skin allergies or rashes: Yes/No
c. Anxiety: Yes/No
d. General weakness or fatigue: Yes/No
e. Any other problem that interferes with your use of a respirator: Yes/No
9. Would you like to talk to the health care professional who will review this questionnaire about your answers to this questionnaire: Yes/No
Questions 10 to 15 below must be answered by every employee who has been selected to use either a full-facepiece respirator or a self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA). For employees who have been selected to use other types of respirators, answering these questions is voluntary.
10. Have you ever lost vision in either eye (temporarily or permanently): Yes/No
11. Do you currently have any of the following vision problems?
a. Wear contact lenses: Yes/No
b. Wear glasses: Yes/No
c. Color blind: Yes/No
d. Any other eye or vision problem: Yes/No
12. Have you ever had an injury to your ears, including a broken ear drum: Yes/No
13. Do you currently have any of the following hearing problems?
a. Difficulty hearing: Yes/No
b. Wear a hearing aid: Yes/No
c. Any other hearing or ear problem: Yes/No
14. Have you ever had a back injury: Yes/No
15. Do you currently have any of the following musculoskeletal problems?
a. Weakness in any of your arms, hands, legs, or feet: Yes/No
b. Back pain: Yes/No
c. Difficulty fully moving your arms and legs: Yes/No
d. Pain or stiffness when you lean forward or backward at the waist: Yes/No
e. Difficulty fully moving your head up or down: Yes/No
f. Difficulty fully moving your head side to side: Yes/No
g. Difficulty bending at your knees: Yes/No
h. Difficulty squatting to the ground: Yes/No
i. Climbing a flight of stairs or a ladder carrying more than 25 lbs: Yes/No
j. Any other muscle or skeletal problem that interferes with using a respirator: Yes/No
Part B Any of the following questions, and other questions not listed, may be added to the questionnaire at the discretion of the health care professional who will review the questionnaire.
1. In your present job, are you working at high altitudes (over 5,000 feet) or in a place that has lower than normal amounts of oxygen: Yes/No
If "yes," do you have feelings of dizziness, shortness of breath, pounding in your chest, or other symptoms when you're working under these conditions: Yes/No
2. At work or at home, have you ever been exposed to hazardous solvents, hazardous airborne chemicals (e.g., gases, fumes, or dust), or have you come into skin contact with hazardous chemicals: Yes/No
If "yes," name the chemicals if you know them:_____________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
3. Have you ever worked with any of the materials, or under any of the conditions, listed below:
a. Asbestos: Yes/No
b. Silica (e.g., in sandblasting): Yes/No
c. Tungsten/cobalt (e.g., grinding or welding this material): Yes/No
d. Beryllium: Yes/No
e. Aluminum: Yes/No
f. Coal (for example, mining): Yes/No
g. Iron: Yes/No
h. Tin: Yes/No
i. Dusty environments: Yes/No
j. Any other hazardous exposures: Yes/No
If "yes," describe these exposures:______________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4. List any second jobs or side businesses you have: _________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
5. List your previous occupations:______________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6. List your current and previous hobbies:________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
7. Have you been in the military services? Yes/No
If "yes," were you exposed to biological or chemical agents (either in training or combat): Yes/No
8. Have you ever worked on a HAZMAT team? Yes/No
9. Other than medications for breathing and lung problems, heart trouble, blood pressure, and seizures mentioned earlier in this questionnaire, are you taking any other medications for any reason (including over-the-counter medications): Yes/No
If "yes," name the medications if you know them: _______________________
10. Will you be using any of the following items with your respirator(s)?
a. HEPA Filters: Yes/No
b. Canisters (for example, gas masks): Yes/No
c. Cartridges: Yes/No
11. How often are you expected to use the respirator(s) (circle "yes" or "no" for all answers that apply to you)?:
a. Escape only (no rescue): Yes/No
b. Emergency rescue only: Yes/No
c. Less than 5 hours per week: Yes/No
d. Less than 2 hours per day: Yes/No
e. 2 to 4 hours per day: Yes/No
f. Over 4 hours per day: Yes/No
12. During the period you are using the respirator(s), is your work effort:
a. Light (less than 200 kcal per hour): Yes/No
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift:____________hrs.____________mins.
Examples of a light work effort are sitting while writing, typing, drafting, or performing light assembly work; or standing while operating a drill press (1-3 lbs.) or controlling machines.
b. Moderate (200 to 350 kcal per hour): Yes/No
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift:____________hrs.____________mins.
Examples of moderate work effort are sitting while nailing or filing; driving a truck or bus in urban traffic; standing while drilling, nailing, performing assembly work, or transferring a moderate load (about 35 lbs.) at trunk level; walking on a level surface about 2 mph or down a 5-degree grade about 3 mph; or pushing a wheelbarrow with a heavy load (about 100 lbs.) on a level surface.
c. Heavy (above 350 kcal per hour): Yes/No
If "yes," how long does this period last during the average shift:____________hrs.____________mins.
Examples of heavy work are lifting a heavy load (about 50 lbs.) from the floor to your waist or shoulder; working on a loading dock; shoveling; standing while bricklaying or chipping castings; walking up an 8-degree grade about 2 mph; climbing stairs with a heavy load (about 50 lbs.).
13. Will you be wearing protective clothing and/or equipment (other than the respirator) when you're using your respirator: Yes/No
If "yes," describe this protective clothing and/or equipment:____________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
14. Will you be working under hot conditions (temperature exceeding 77 °F): Yes/No
15. Will you be working under humid conditions: Yes/No
16. Describe the work you'll be doing while you're using your respirator(s):
_____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
17. Describe any special or hazardous conditions you might encounter when you're using your respirator(s) (for example, confined spaces, life-threatening gases):
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
18. Provide the following information, if you know it, for each toxic substance that you'll be exposed to when you're using your respirator(s):
Name of the first toxic substance:____________________________________________
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift:____________________________________
Duration of exposure per shift:______________________________________________
Name of the second toxic substance:__________________________________________
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift:____________________________________
Duration of exposure per shift:______________________________________________
Name of the third toxic substance:____________________________________________
Estimated maximum exposure level per shift:__________________________________
Duration of exposure per shift:______________________________________________
The name of any other toxic substances that you'll be exposed to while using your respirator:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
19. Describe any special responsibilities you'll have while using your respirator(s) that may affect the safety and well-being of others (for example, rescue, security):
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
[63 FR 1152, Jan. 8, 1998; 63 FR 20098, April 23, 1998; 76 FR 33607, June 8, 2011; 77 FR 46949, Aug. 7, 2012]
